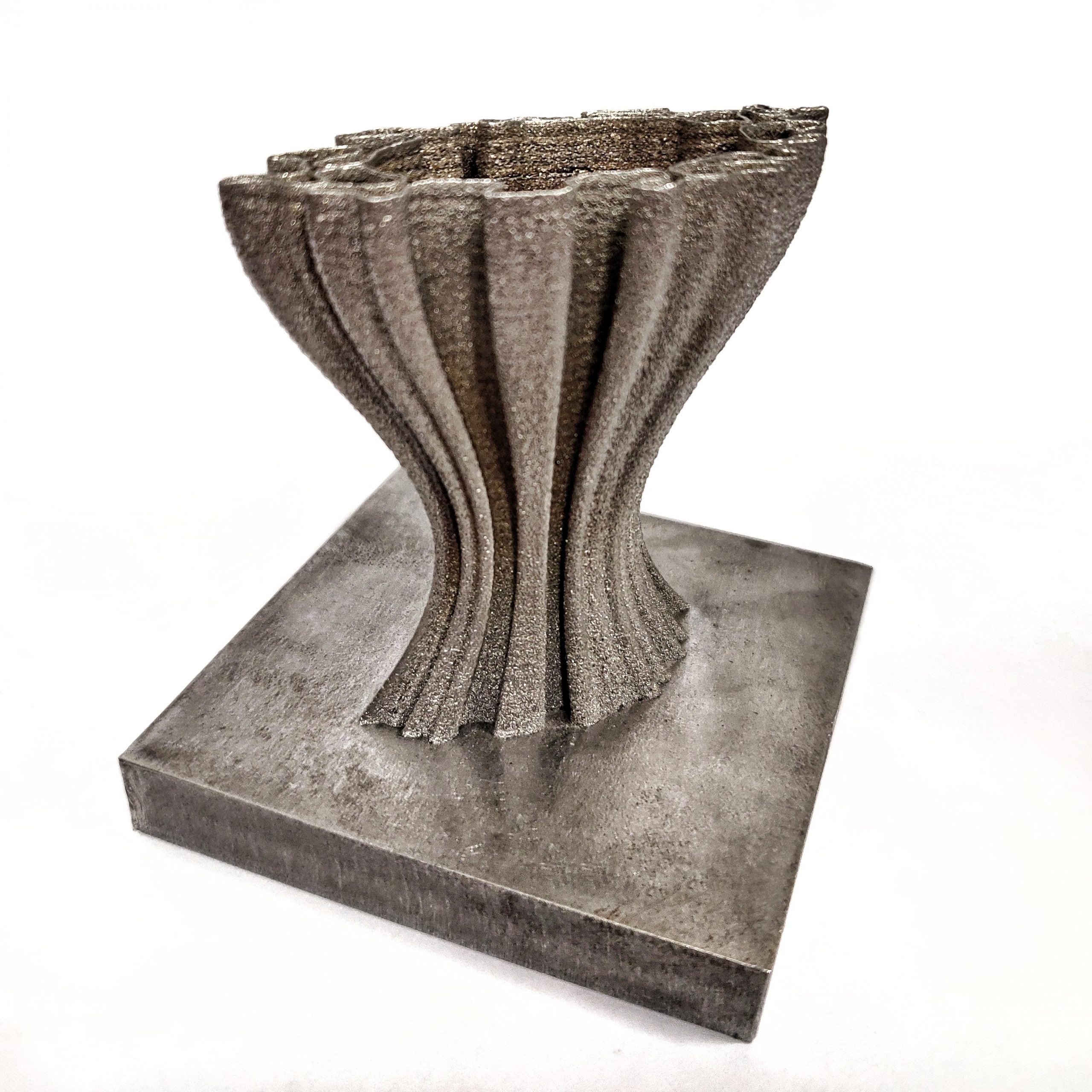
3D printing is sometimes referred to as Additive Manufacturing (AM). In 3D printing, one creates a design of an object using software, and the 3D printer creates the object by adding layer upon layer of material until the shape of the object is formed.
There are several 3D printing technologies, they are; Stereolithography (SLA), Digital Light Processing (DLP), Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electronic Beam Melting (EBM), Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM).
The main differences between processes are in the way layers are deposited to create parts and in the materials that are used. Each method has its own advantages and drawbacks, which is why some companies offer a choice of powder and polymer for the material used to build the object. Others sometimes use standard, off-the-shelf business paper as the build material to produce a durable prototype. The main considerations in choosing a machine are generally speed, cost of the printed prototype, the choice and cost of materials along with colour capabilities. Printers that work directly with metals are generally expensive. However less expensive printers can be used to make a mold, which is then used to make metal parts.